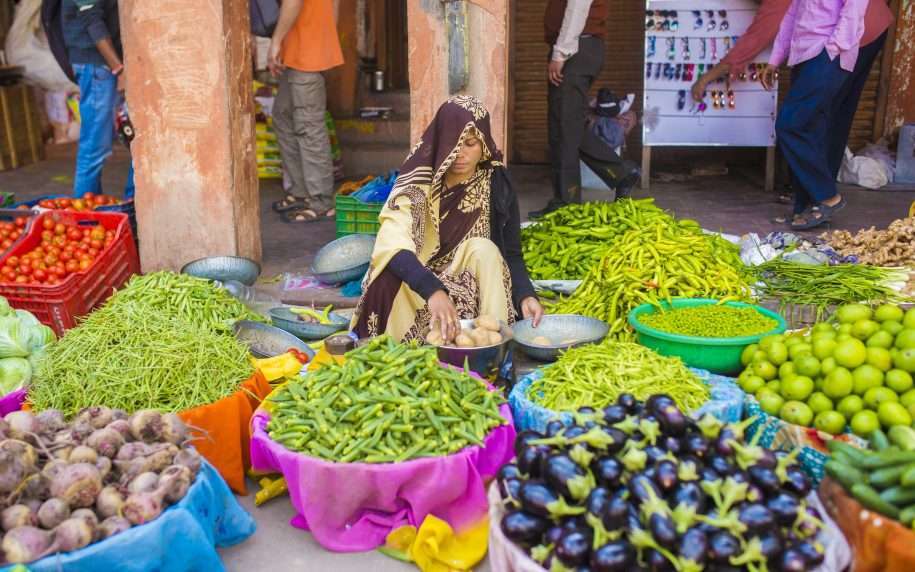
Figure: Snapshot of MSME Landscape in India (Authors own compilation.)
Source: Make in India, MSME Sector-Achievement Report 2017
of easy formal credit sources is another possible area of intervention. Credit access can be improved by promoting financial inclusion, making finance affordable and by facilitating formalization of businesses. Capacity building by emphasizing on skill development of marginalized communities, business management training for existing enterprises and support in technology upgradation can be a motivating factor, with financial literacy in India being as low as 20 per cent. Most importantly, improved research and development is of key importance with the global importance MSMEs have gained in 2017. Creation of updated databases and strengthening of research and development techniques collected by civil society is important to be used as foundations of great policy initiatives and in further implementation of the same.
|
What needs to be done to further strengthen the MSME sector in India?
|
|
1.Capacity building- Skill Development, Business management, Technology Upgradation
|
|
2.Credit Access –Financial literacy training and inclusion, Affordable Finance, Formal institutions
|
|
3. Easy market linkages- Showcase competencies, Policy support, Formalization
|
|
4. Employment generation- Support for Youth Start-ups, Women Empowerment, Promoting rural industries
|
|
5.Improved R&D– Creation of databases, Strengthening of Research and Development
|
Figure: Recommendations for MSME sector in India (Authors own compilation.)
MSME Sector-Achievement Report 2017. Make in India.
Annual Report 2015-16. Delhi: Ministry of MSME.
SDG Mapping- Status Draft Report, NITI Aayog, New Delhi.
MSME Country Indicators. IFC, World Bank. (2010, August).
MSME Finance in India. International Finance Corporation. (2012).
Recommendations of the Inter-Ministerial Committee for Accelerating Manufacturing, Ministry of MSME, (2013).