“Living in a tier-2 city in the state of Rajasthan in India, I had to take half a day off from work to apply for an Aadhaar card. I had to travel to the Aadhaar center, which was about 7kms away, stand in line for one hour for my turn to come, only to realize that the machine was not accepting my iris scan. The three officials at the center could not figure out the problem, after struggling for 20 minutes. I was told to wait for another half hour, for the machine to start working. After half an hour, the machine started working and my application was submitted. The entire process took 4 hours. The majority of people living in rural areas do not have the luxury to step away from their work and lose out on daily wages.
The time spent on this process can be minimized for government entitlements that require in-person presence of the applicant and eliminated for entitlements that do not require the in-person presence of the applicant” – Anoushaka
Poor households often rely on government entitlements for mitigating risk and livelihood development. With the aim of increasing information about and uptake of government entitlements, and with the support of the State Rural Livelihoods Mission (SRLM) in the state of Chhattisgarh, IWWAGE – an initiative of LEAD at Krea University, and Haqdarshak Empowerment Solutions Private Limited (HESPL), is implementing a project for promoting government entitlements through women self-help group (SHG) members as agents. As part of this project, self-help group (SHG) members receive training on how to use a digital application, Haqdarshak, which provides a ready reference of more than 200 central and state government welfare programs, their benefits, eligibility criteria, documents required, and the application process for each scheme. The trained agents offer door-to-door services to their respective communities using the app to support households to gather information and apply for government programs, for a small fee.
The project is being implemented in four districts of Chhattisgarh (Raipur, Rajnandgaon, Dhamtari and Gariyaband) and over the past year around 2,700 SHG women have been trained to become Haqdarshak agents. Among all of the trained women around 1,000 performed their duty actively and have received over 100,000 applications for a wide range of government entitlements[i].
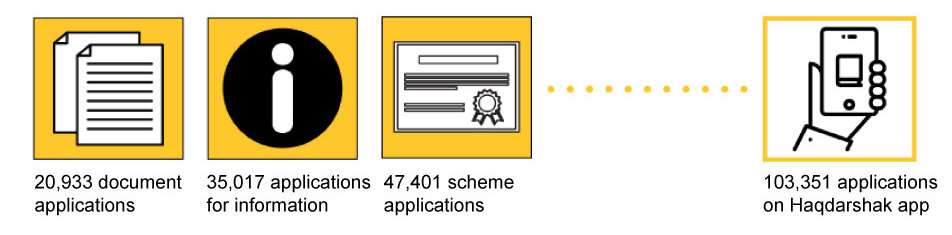
A deep-dive into these 100,000 applications reveals several interesting trends:
- 34% of the total applications are for COVID-19 related informational schemes. These include availability of free ration at PDS shops, cash transfers to women PMJDY account holders, distribution of free food packets for children enrolled in government anganwadis, and availability of free gas cylinders under the Ujjwala Yojana. Providing information to the rural poor about the availability and the mode of access for these additional benefits is an important step in ensuring that the benefits reach the intended beneficiaries. In such situations, the Haqdarshika’s role was to inform citizens enrolled in these schemes of the additional benefits available they can avail and, when necessary, support them to access these benefits.
- PAN cards are the most sought-after document, accounting for 80% of the total applications for documents. Insights from our fieldwork suggest that people in rural areas perceive the PAN card as a document required for opening of bank accounts and it is also promoted as such by many application touch-points.
- Among welfare schemes, insurance programs like the Pradhan Mantri Bima Suraksha Yojana (PMSBY), Ayushman Bharat and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) are the most popular schemes among applicants.
Among the four districts in which the program was implemented, Raipur district accounted for around 48% of the 100,000 applications, followed by 38% from Rajnandgaon, and the remaining 14% of the applications were from the Dhamtari and Gariyaband districts. However, an important caveat is that the program targeted Raipur district first, which means that the intervention has been running in the district for a much longer time. The intervention has also targeted fewer blocks in Dhamtari and Gariyaband, as compared to Rajnandgaon and Raipur districts.
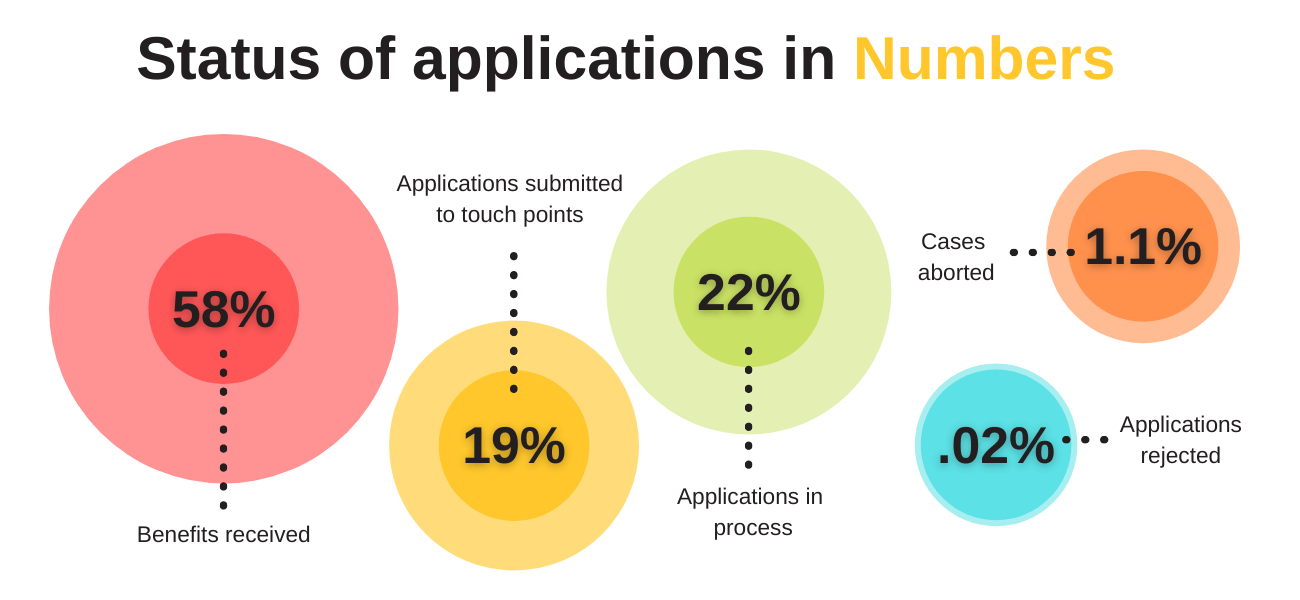
Reaching the 100,000 applications mark on the Haqdarshak platform has been an important milestone for the project. However, there have been several challenges in implementation along the way and the program team is working towards developing solutions to address these.
Dropout of Haqdarshikas from the program
Of the 2,700 women trained to be Haqdarshikas, only 603 are active as of September 2020. A Haqdarshika is considered ‘active’ if she has processed at least one application in a given month. Some of the factors which may account for this trend are:
- Some of the training participants might not pass a post-assessment test, which is required to conduct transactions on the platform.
- 60 to 80 percent of the agents drop out after the fourth month of activity. This could be due to saturation of applications for schemes and documents for which Haqdarshikas (HDs) have most information. Refresher trainings are being conducted with HDs who dropped out of the program, to overcome this challenge.
- Other reasons include damages to their smartphone, shared usage of smartphone resulting in non-availability of the phone for the Haqdarshikas, restrictions on mobility from their families, lack of entrepreneurial spirit etc. This is clearly an issue of targeting. Selecting suitable candidates for the training requires time and effort, since potential participants need to be screened against certain minimum requirements and informed about the expected commitment, type of work, and remuneration of the program. Ensuring greater buy-in and providing a higher degree of support to local government officials is essential to make any progress on this issue.
Long processing time for applications
While the 100,000 applications milestone suggests that there is a high demand for government entitlements among rural households, not all the applications have translated to benefits received by the citizens. This could potentially be explained by the long processing time and procedural delays for certain schemes and documents. The project team is exploring ways to delve deeper into the reasons for delay and also ways to tackle this challenge.
Technology needs a sustained value proposition
Another reason why we see less than 100% conversion of applications submitted to benefits received is that Haqdarshikas at times do not update the status of the application itself. This indicates that while the citizen may have received the benefit, the status displayed on the app shows that the application is ‘pending’. This could be due to the fact that Haqdarshikas do not follow up on the processed applications in a timely manner or to the citizens not feeling comfortable providing proof of receipt of the document or scheme they applied for due to privacy concerns. Both instances point to a lack of practical and/or material incentives to update the status of the applications, besides the Haqdarshikas’ own diligence. This issue could be addressed, for example, by a change in the remuneration structure of the model or by increased integration of the app in the government’s own application system, thus reducing the need for manual inputs.
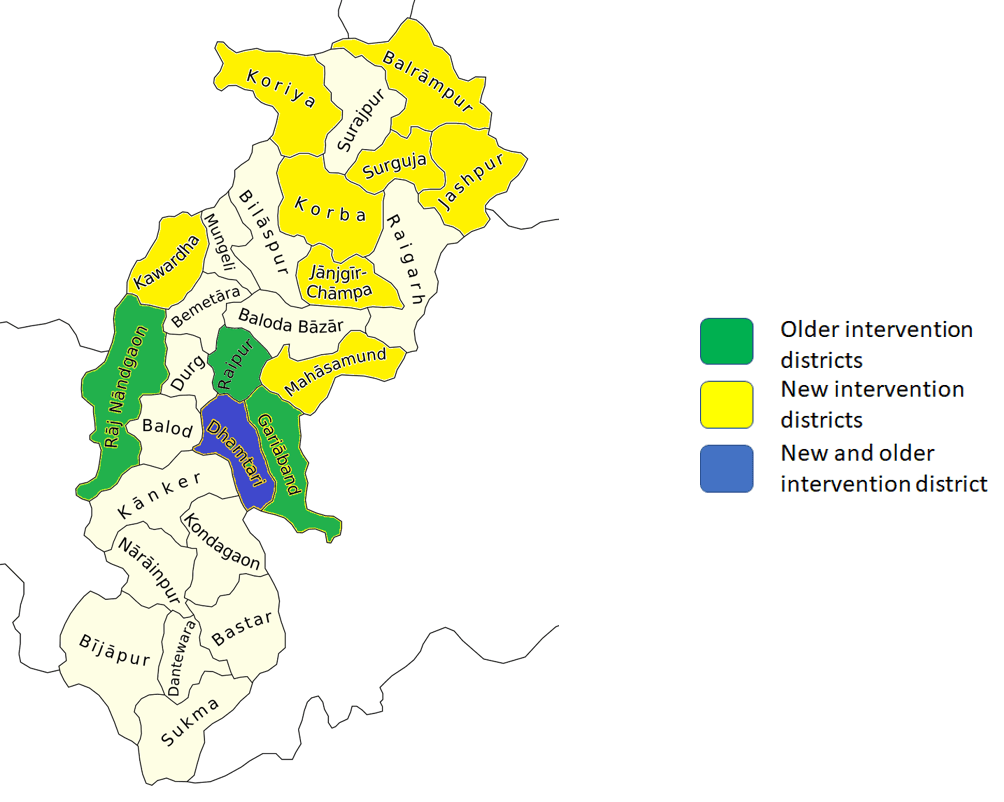
In the coming months, the Haqdarshak program will be scaled up to 21 different blocks in nine additional districts of Chhattisgarh. In these blocks, with the support of CGSRLM, the implementation will focus on Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) and Persons with Disabilities (PWDs) to improve their access to information and in turn, government entitlements.
[i] [i] These applications were received between June 2019 and September 2020.
Anoushaka Chandrashekar is a Project Manager with LEAD at Krea University and Raka De is a Research Associate with LEAD at Krea University.





