Empowerment
Through
Evidence
LEAD’s Udyogini initiative aims to create a curated platform to share lessons and findings from our work on women entrepreneurship, with the intent of building evidence to inform policies and accelerate growth.

MSME Sector at a glance: India’s growth story
(2015-16)
Total Enterprises
(2019)
GDP contribution of MSMEs
(2019)
Export contribution of MSMEs
(2015-16)
Jobs created by MSMEs
The sector’s contribution to GDP and global export market is borne by a small portion of registered (30%) and large-scale enterprises but this contribution has remained unchanged over time.
Moreover, out of the total 63 million enterprises, over 98% are run by solopreneurs and ~70% of the enterprises remain informal and unregistered.
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), 6th Economic Census (2013-14), MOSPI, ADB and IFC estimates (2021)

MSME Sector at a glance: India’s growth story
MSME’s Export and GDP Contribution (%)
MSME GDP Contribution
MSME Exports
The sector’s contribution to GDP and global export market is borne by a small portion of registered (30%) and large-scale enterprises but this contribution has remained unchanged over time.
Moreover, out of the total 63 million enterprises, over 98% are run by solopreneurs and ~70% of the enterprises remain informal and unregistered.
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), 6th Economic Census (2013-14)
An uneven playing field
The disparity is starker for women in business
Just
1 in 5
entrepreneurs is a woman.
and 65.3% of them are ‘homepreneurs’ – running businesses out of their own homes, further invisibilising their contribution and voice in India’s entrepreneurship narrative.
Source: MSME Ministry's Annual Report 2020-21, 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16)





These businesses are concentrated in gendered, traditional sectors across rural and urban geographies.
Female
40.3%
20.7%
7.1%
5.6%
5.4%
5.3%
2.9%
2.2%
1.6%
1.0%
8.0%
Apparel
Retail
Personal Services*
Education
Restaurant
Tobacco
Food
Human Health
Other Manufacturing^
Wood
Others
7.5%
26.2%
4.8%
2.8%
8.8%
0.3%
5.6%
3.1%
1.4%
1.7%
38.0%
Male
Top 10 industries in India for female entrepreneurs
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), In-house analysis
2015
Footnote: .
*Includes Salon, Laundry, Housekeeping Services etc.
^Includes jewellery and imitation jewellery manufacturing, musical instruments, sports goods, toys etc.
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), In-house analysis, Mehrotra (2019)
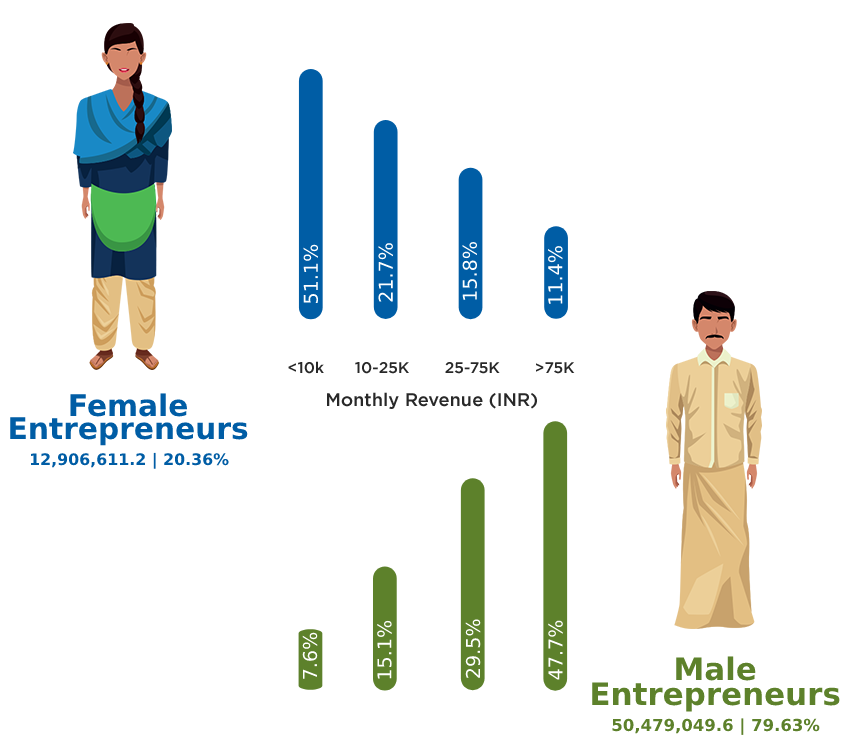
Moreover, their representation remains highest in small-scale and low-revenue businesses, unlike their male counterparts, constraining their growth, and pushing them to stay small.
Investing In Women: A Compelling Economic Case
01
More women-led businesses = higher economic growth
Women-led businesses currently contribute to only 3% of the total industrial output and are an untapped economic opportunity. Increasing their presence in productive sectors can lead to exponential economic gains (IFC 2017).
02
Investing in women-led businesses is investing in the ecosystem
Currently women-led businesses provide employment to 27 million workers. An uptick in women entrepreneurship is well-positioned to drive significant improvement in job creation.
Source: IFC (2017)
Women-led businesses are reliable, resilient and adaptable
- Regardless of market disruptions and economic shocks women-led businesses remain resilient, showcasing ingenuity and adaptability in running their businesses (Narasimhan et al, 2021)
- Higher credit consciousness, better credit scores
and lower delinquency rates vs. male peers (TransUnion CIBIL and CRIF HighMark,
2022)
03
What is holding them back?
YET, from ideation to scale-up the barriers to graduation are immense
Literature highlights various factors that drive this phenomenon
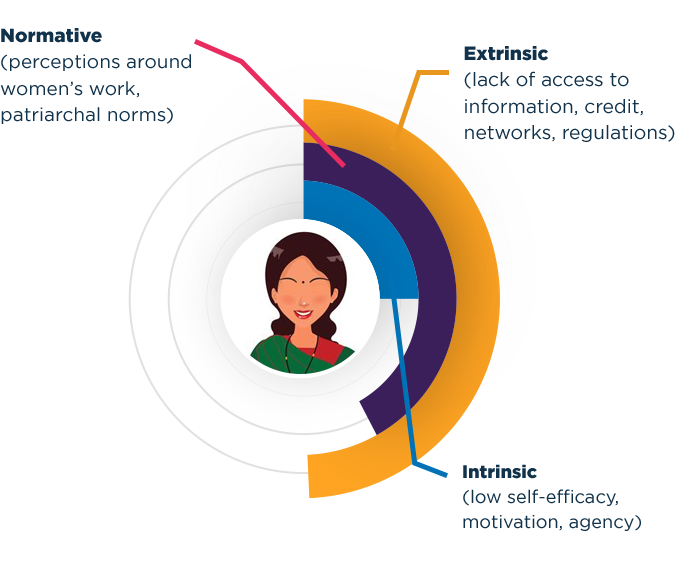

Low confidence in skills and ability to make decisions, affecting their motivation to start a business

Lack of support from family and friends

Restrictive social and cultural norms, limiting entrepreneurs to traditional, conventional sectors

Poor access to timely finance, due to lack of collateral and credit histories


Double-burden takes away their time from business

Lack of business acumen and skills, and limited opportunities for upskilling

Limited access to relevant market information affecting business performance

Mobility constraints affecting market reach


Weak access to technology pushing businesses to stay small

Limited networking and mentoring opportunities curtailing business growth

Restrictive and complex regulatory procedures that curtail formalisation and growth

Lack of business innovation, limiting opportunities to scale business

Encouraging
entrepreneurship

ENCOURAGING ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Insights that address individual, social and normative barriers so that women can pursue entrepreneurship in conventional and new sectors
Bolstering
Business Acumen

BOLSTERING BUSINESS ACUMEN
Insights equipping women entrepreneurs with information, skills, and resources needed to optimise business outcomes and scale-up
Creating an
Enabling Environment

CREATING AN ENABLING ENVIRONMENT
Insights on systemic and policy changes that can improve the ease of doing business for women and create enabling conditions that encourage take-up in entrepreneurship

Explore
Our Work
From Barriers To Breakthroughs
Insights-driven Future of Women Entrepreneurship

Empowerment
Through
Evidence
LEAD’s Udyogini initiative aims to create a curated platform to share lessons and findings from our work on women entrepreneurship, with the intent of building evidence to inform policies and accelerate growth.

MSME Sector at a glance: India’s growth story

The sector’s contribution to GDP and global export market is borne by a small portion of registered (30%) and large-scale enterprises but this contribution has remained unchanged over time.
Moreover, out of the total 63 million enterprises, over 98% are run by solopreneurs and ~70% of the enterprises remain informal and unregistered.
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), 6th Economic Census (2013-14), MOSPI, ADB and IFC estimates (2021)
An uneven playing field
The disparity is starker for women in business
Just
1 in 5
entrepreneurs are women.
and 65.3% of them are ‘homepreneurs’ – running businesses out of their own homes, further invisibilising their contribution and voice in India’s entrepreneurship narrative.
Source: MSME Ministry's Annual Report 2020-21, 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16)





These businesses are concentrated in gendered, traditional sectors across rural and urban geographies.
40.2%
20.7%
7.9%
7.1%
5.5%
5.4%
5.2%
5.2%
2.8%
1.5%
1%
Apparel
Retail
Personal Services*
Education
Restaurant
Tobacco
Food
Human Health
Other Manufacturing^
Wood
Others
2015
7.5%
26.2%
4.8%
2.8%
8.8%
0.3%
5.6%
3.1%
1.4%
1.7%
38.0%
Female
Male
Top 10 industries in India for female entrepreneurs
Footnote: .
*Includes Salon, Laundry, Housekeeping Services etc.
^Includes jewellery and imitation jewellery manufacturing, musical instruments, sports goods, toys etc.
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), In-house analysis

Moreover, their representation remains highest in small-scale and low-revenue businesses, unlike their male counterparts, constraining their growth, and pushing them to stay small.
Source: 73rd National Sample Survey (2015-16), In-house analysis, Mehrotra (2019)
Source: IFC (2017)
Investing In Women:
A Compelling Economic Case
01
More women-led businesses = higher economic growth
Women-led businesses currently contribute to only 3% of the total industrial output and are an untapped economic opportunity. Increasing their presence in productive sectors can lead to exponential economic gains (IFC 2017).

02
Investing in women-led businesses is investing in the ecosystem
Currently women-led businesses provide employment to 27 million workers. An uptick in women entrepreneurship is well-positioned to drive significant improvement in job creation.

03
Women-led businesses are reliable, resilient and adaptable
- Regardless of market disruptions and economic shocks women-led businesses remain resilient, showcasing ingenuity and adaptability in running their businesses (Narasimhan et al, 2021)
- Higher credit consciousness, better credit scores
and lower delinquency rates vs. male peers (TransUnion CIBIL and CRIF HighMark,
2022)
What is holding them back?
YET, from ideation to scale-up the barriers to graduation are immense
Literature highlights various factors that drive this phenomenon

Barriers to entry
Low confidence in skills and ability to make decisions, affecting their motivation to start a business
Lack of support from family and friends
Restrictive social and cultural norms, limiting entrepreneurs to traditional, conventional sectors
Poor access to timely finance, due to lack of collateral and credit histories
Barriers to sustain
Lack of business acumen and skills, and limited opportunities for upskilling
Double-burden takes away their time from business
Limited access to relevant market information affecting business performance
Mobility constraints affecting market reach
Barriers to growth
Limited networking and mentoring opportunities curtailing business growth
Weak access to technology pushing businesses to stay small
Lack of business innovation, limiting opportunities to scale business
Restrictive and complex regulatory procedures that curtail formalisation and growth
Encouraging
entrepreneurship

ENCOURAGING ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Insights that address individual, social and normative barriers so that women can pursue entrepreneurship in conventional and new sectors
Bolstering
Business Acumen

BOLSTERING BUSINESS ACUMEN
Insights equipping women entrepreneurs with information, skills, and resources needed to optimise business outcomes and scale-up
Creating an
Enabling Environment

CREATING AN ENABLING ENVIRONMENT
Insights on systemic and policy changes that can improve the ease of doing business for women and create enabling conditions that encourage take-up in entrepreneurship